Brain-computer interfaces (BCIs) enable direct and bidirectional communication between the human brain and computers. The analysis and interpretation of brain signals, which provide valuable information about mental state and brain activity, pose challenges due to their non-stationarity and vulnerability to various interferences. Consequently, research in the BCI field emphasizes the integration of artificial intelligence (AI), particularly in five key areas: calibration, noise reduction, communication, mental state estimation, and motor imagery. The utilization of AI algorithms and machine learning has shown great promise in these applications, primarily because of their capacity to predict and learn from past experiences. As a result, implementing these technologies within medical contexts can provide more accurate insights into the mental state of individuals, mitigate the effects of severe illnesses, and enhance the quality of life for disabled patients.
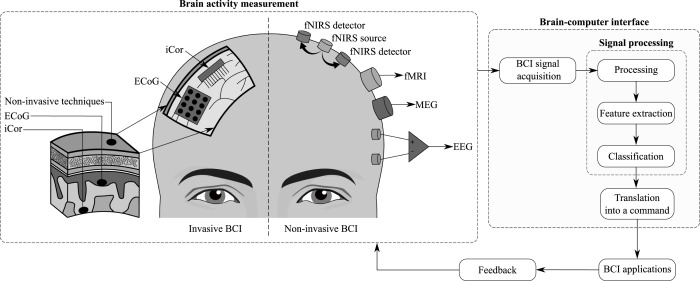
New paper regarding Brain-Computer Interfaces published:
Barnova, K., Mikolasova, M., Kahankova, R. V., Jaros, R., Kawala-Sterniuk, A., Snasel, V., … & Martinek, R. (2023). Implementation of artificial intelligence and machine learning-based methods in brain-computer interaction. Computers in Biology and Medicine, 107135.
https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0010482523006005
